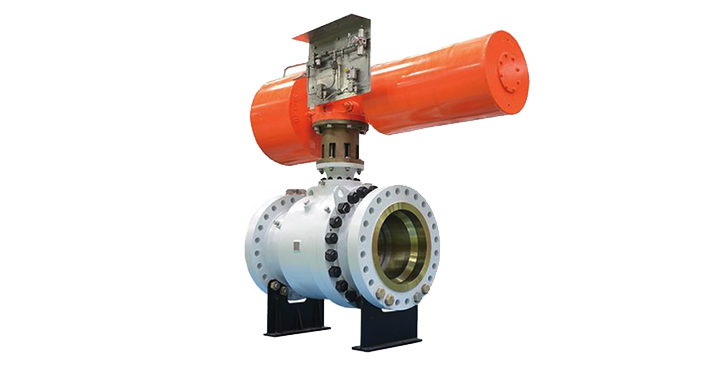
ACTUATOR
An actuator is a part of a device or machine that helps it to achieve physical movements by converting energy, often electrical, air, or hydraulic, into mechanical force. Simply put, it is the component in any machine that enables movement.
TYPES OF ACTUATOR MOVEMENTS
A rotary actuator is an actuator that produces a rotary motion or torque.
The simplest actuator is purely mechanical, where linear motion in one direction gives rise to rotation. The most common actuators are electrically powered; others may be powered pneumatically or hydraulically, or use energy stored in springs.
The motion produced by an actuator may be either continuous rotation, as for an electric motor, or movement to a fixed angular position as for servomotors and stepper motors. A further form, the torque motor, does not necessarily produce any rotation but merely generates a precise torque which then either causes rotation or is balanced by some opposing torque.
A linear actuator is an actuator that creates motion in a straight line, in contrast to the circular motion of a conventional electric motor. … Hydraulic or pneumatic cylinders inherently produce linear motion. Many other mechanisms are used to generate linear motion from a rotating motor.
Double-acting actuators have air or liquid supplied to both sides of the piston with one side at higher pressure, which achieves the movement required to actuate the valve. This configuration uses pneumatic or hydraulic pressure of the air or liquid energy to open and close the valve
Spring-return actuators have air or liquid supplied to only one side of the piston, and the energy to move the mechanisms comes from a spring on the opposite side. This configuration uses pneumatic or hydraulic pressure of the air or liquid to open or close the valve, and a spring affects the opposite motion
PRODUCT DETAILS
Material of Construction
Anodized Aluminium, Cast Iron, SS
Certification
SIL
Type
Pneumatic, Electrical, Hydraulic